北京邮电大学 信息光子学与光通信全国重点实验室,北京 100876
无源光网络(PON)凭借其大带宽、低成本和抗电磁干扰等优势,被认为是下一代工业互联网的重要组网技术之一。然而,以“带宽提升”为主要技术发展思路的常规PON,其传输控制机制难以满足以“时间敏感”为特征的高品质工业业务传输需求,对常规PON的网络传输能力提出了重要挑战,迫使其融入新的特性,即确定性。文章以时分复用(TDM)-PON为主要研究对象,首先阐述了工业互联网的业务特征及传输需求,分析了工业互联场景下常规TDM-PON面临的两大技术挑战:一是传统带宽分配方案引起的时延不确定性;二是队列调度机制僵化引起的时延不确定性。围绕上述挑战,文章介绍了提升TDM-PON确定性网络传输能力的关键技术,如协作传输接口、单帧多突发和确定性带宽分配(DetBA)等。其次,文章介绍了一种基于网络演算的时延边界建模思路作为确定性工业PON系统设计与性能评估的理论模型。最后,文章从业务层、媒质接入控制(MAC)层、物理层及控制管理平面等多个角度探讨了确定性工业PON的潜在技术及发展方向。
工业无源光网络 确定性网络传输技术 确定性带宽分配 网络演算 industrial PON deterministic network transmission technology DetBA network calculus 光通信研究
2024, 50(1): 23016801

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, School of Information and Communication Engineering, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
This Letter proposes a model of indoor visible light communication (VLC) heterogeneous networks entirely based on LEDs with different specifications and applies non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) to it because of the narrow modulation bandwidth of LEDs. Moreover, a user-grouping scheme that is based on matching theory is proposed to improve the network achievable sum rate. Simulation results indicate that when each NOMA cluster contains 6 users, the proposed scheme has a 49.54% sum-rate enhancement compared with the traditional user-grouping scheme. As the number of users in each NOMA cluster increases, the proposed scheme performs better at the cost of computational complexity.
visible light communication non-orthogonal multiple access matching theory user grouping Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(6): 060602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, School of Information and Communication Engineering, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
2 State Key Laboratory for Artificial Microstructure and Mesoscopic Physics, School of Physics, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
3 Frontiers Science Center for Nano-optoelectronics & Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter, Beijing 100871, China
4 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
5 Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences, Beijing 100193, China
The ability to sense dynamic biochemical reactions and material processes is particularly crucial for a wide range of applications, such as early-stage disease diagnosis and biomedicine development. Optical microcavities-based label-free biosensors are renowned for ultrahigh sensitivities, and the detection limit has reached a single nanoparticle/molecule level. In particular, a microbubble resonator combined with an ultrahigh quality factor () and inherent microfluidic channel is an intriguing platform for optical biosensing in an aqueous environment. In this work, an ultrahigh microbubble resonator-based sensor is used to characterize dynamic phase transition of a thermosensitive hydrogel. Experimentally, by monitoring resonance wavelength shift and linewidth broadening, we (for the first time to our knowledge) reveal that the refractive index is increased and light scattering is enhanced simultaneously during the hydrogel hydrophobic transition process. The platform demonstrated here paves the way to microfluidical biochemical dynamic detection and can be further adapted to investigating single-molecule kinetics.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(4): 04000497

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Information and Communication Engineering, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
3 State Key Laboratory for Mesoscopic Physics, School of Physics, Peking University, Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter, Beijing 100871, China
4 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan, Shanxi 030006, China
Optical trapping techniques are of great interest since they have the advantage of enabling the direct handling of nanoparticles. Among various optical trapping systems, photonic crystal nanobeam cavities have attracted great attention for integrated on-chip trapping and manipulation. However, optical trapping with high efficiency and low input power is still a big challenge in nanobeam cavities because most of the light energy is confined within the solid dielectric region. To this end, by incorporating a nanoslotted structure into an ultracompact one-dimensional photonic crystal nanobeam cavity structure, we design a promising on-chip device with ultralarge trapping potential depth to enhance the optical trapping characteristic of the cavity. In this work, we first provide a systematic analysis of the optical trapping force for an airborne polystyrene (PS) nanoparticle trapped in a cavity model. Then, to validate the theoretical analysis, the numerical simulation proof is demonstrated in detail by using the three-dimensional finite element method. For trapping a PS nanoparticle of 10 nm radius within the air-slot, a maximum trapping force as high as 8.28 nN/mW and a depth of trapping potential as large as 1.15×105 kBT mW 1 are obtained, where kB is the Boltzmann constant and T is the system temperature. We estimate a lateral trapping stiffness of 167.17 pN·nm 1· mW 1 for a 10 nm radius PS nanoparticle along the cavity x-axis, more than two orders of magnitude higher than previously demonstrated on-chip, near field traps. Moreover, the threshold power for stable trapping as low as 0.087 μW is achieved. In addition, trapping of a single 25 nm radius PS nanoparticle causes a 0.6 nm redshift in peak wavelength. Thus, the proposed cavity device can be used to detect single nanoparticle trapping by monitoring the resonant peak wavelength shift. We believe that the architecture with features of an ultracompact footprint, high integrability with optical waveguides/circuits, and efficient trapping demonstrated here will provide a promising candidate for developing a lab-on-a-chip device with versatile functionalities.
Integrated optics devices Nanophotonics and photonic crystals Optical tweezers or optical manipulation Laser trapping Photonic crystals Resonators Photonics Research
2018, 6(2): 02000099

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (BUPT), Beijing 100876, China
To extensively deploy quantum key distribution (QKD) systems, copropagating with classical channels on the same fiber using wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology becomes a critical issue. We propose a user-based channel-interleaving WDM scheme with unequal frequency spacing (UFS-iWDM) to reduce the impairment on the quantum channels induced by four-wave mixing (FWM), and theoretically analyze its impact on quantum bit error rate (QBER). Numerical simulation results show that a UFS-iWDM can significantly reduce the FWM noise and improve QBER compared with the corresponding WDM scheme with equal frequency spacing (EFS), especially in the case of nonzero dispersion shifted fiber.
270.5565 Quantum communications 060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.4510 Optical communications Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(6): 060602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
Visible light positioning (VLP) is an emerging candidate for indoor positioning, which can simultaneously meet the requirements for accuracy, cost, coverage area, and security. However, intercell interference caused by light intensity superposition limits the application of VLP. In this Letter, we propose a united block sequence mapping (UBSM)-based VLP that utilizes superposition to integrate the multidimensional information from dense small cells into 2D information. The experimental result shows that UBSM-based VLP can achieve an accuracy of 1.5 cm with a 0.4 m row spacing and 0.35 m column spacing of LED lights.
060.4510 Optical communications 200.2605 Free-space optical communication 230.3670 Light-emitting diodes Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(7): 070601
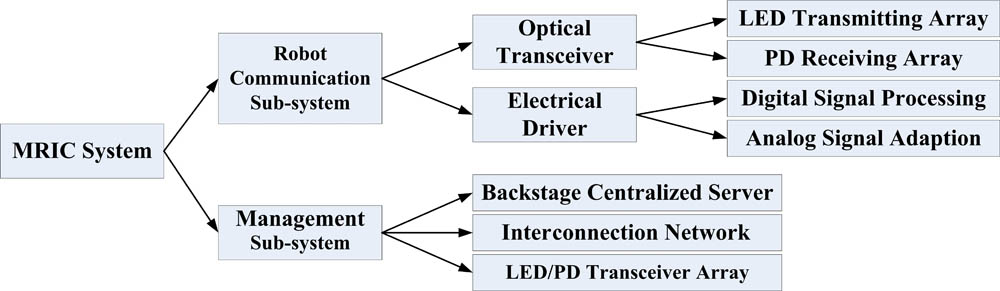
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications (IPOC), Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
2 Beijing University of Technology, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Future Internet Technology, Beijing 100124, China
Multi-robot coordination (MRC) is a key challenge for complex artificial intelligence systems, and conventional wireless-communication-based MRC mechanisms that cannot be deployed in radio-frequency-limited environments. In this Letter, we present a promising solution that utilizes indoor omni-directional visible light communication (VLC) technology to realize efficient multi-robot intelligent coordination (MRIC). The specific design is presented along with the implemental details of a practical MRIC experimental platform. The experimental results show that a 50 Mb/s on-off-keying-based omni-directional VLC can be realized with an effective distance of 2.3 m and a bit error rate of <10 6 in the proposed MRIC platform.
230.3670 Light-emitting diodes 060.2605 Free-space optical communication Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(10): 102301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
In visible light communication, orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) is an effective approach to improve the system speed. However, the nonlinearity of the light-emitting diode (LED) suppresses the transmission performance. The low-frequency part of the transmitted signal from LED suffers more from nonlinearity. Therefore, a pre-equalization scheme which suppresses the low frequency part of the OFDM signal and enhances the high frequency part can decrease the impact of LED nonlinearity. The experimental results show that the bit-error rate performance is largely enhanced by the pre-compensation.
230.4320 Nonlinear optical devices 230.3670 Light-emitting diodes 060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(7): 072302
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communication, School of Information and Communication Engineering, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
2 Institute of Innovative Science and Technology, Tokai University, Japan
We experimentally demonstrate multichannel wavelength multicasting for two nonreturn-to-zero quadrature phase-shift keying (NRZ-QPSK) channels based on four-wave mixing (FWM) in semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA). Through the interaction with the two pumps in SOA, the input two 25 Gb/s NRZ-QPSK channels are successfully simultaneously multicast to five and two new wavelengths, respectively. All the multicast channels are with a power penalty less than 2.5 dB at a bit error rate (BER) of 10-3. A characterization of the system performance using conversion efficiency and BER as figures-of-merit in terms of pump and signal powers is also presented. The results indicate that the pump and signal powers can be optimized to eliminate the introduced deleterious nonlinear components. The wavelengths of the two NRZ-QPSK channels and the two pumps need to be specified to avoid the crosstalk induced by high-order FWM.
060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.4255 Networks, multicast 190.4380 Nonlinear optics, four-wave mixing Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(1): 010601





